tree in bud lesion
Tree-in-bud sign is not generally visible on plain radiographs 2It is usually visible on standard CT however it is best seen on HRCT chest. The connection to opacified or thickened branching structures extends.

Areas Showing A Mosaic Pattern Of Attenuation And Tree In Bud Opacities Download Scientific Diagram
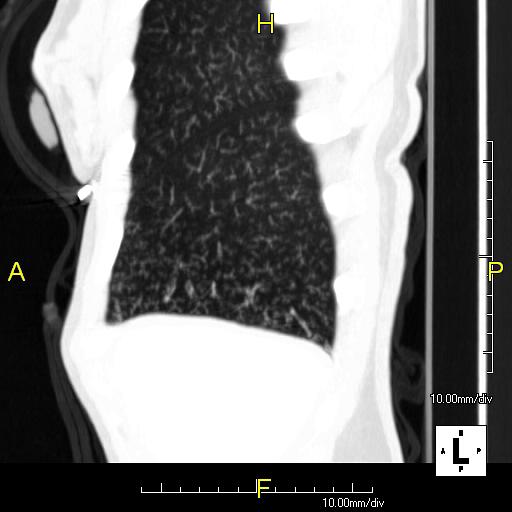
The tree-in-bud sign on thin-section CT is characterized by well-defined small centrilobular nodules and linear opacities with multiple branching sites thus.
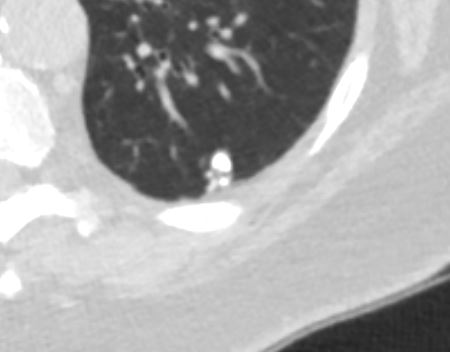
. The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly observed in CT of the lungs because it consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft tissue attenuation connected to multiple. Tree-in-bud refers to small airway at the bronchiole level involvement of lesions resulting in expansion of the airway and infiltration of pathological substances into the tube. By Matt Oct 16 2022 Mast Trees.
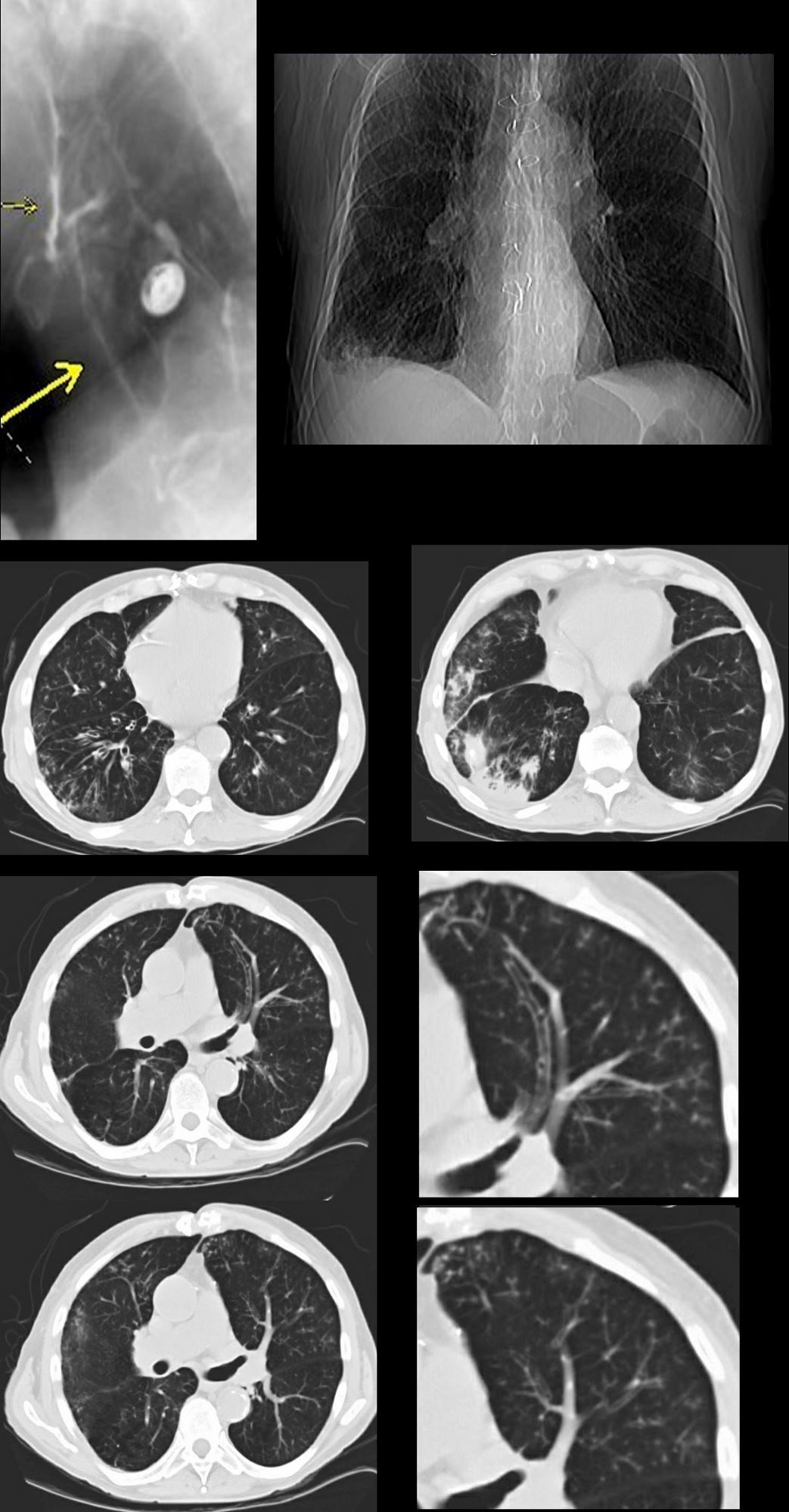
In the 26 patients. Centrilobular nodules with a linear branching pattern are consistent with tree-in-bud appearance in a patient with endobronchial spreading of post-primary tuberculosis. At examination with CT centrilobular lesions nodules or branching linear structures 2-4 mm in diameter were most commonly seen n 39 95.
We investigated the pathological basis of. Tree-in-bud sign refers to the condition in which small centrilobular nodules less than 10 mm in diameter are associated with centrilobular branching nodular structures 1. The peculiarity of the case was that there were streaky areas of enhancement around the lesion in the brain parenchyma which resembled tree-in-bud like appearance.
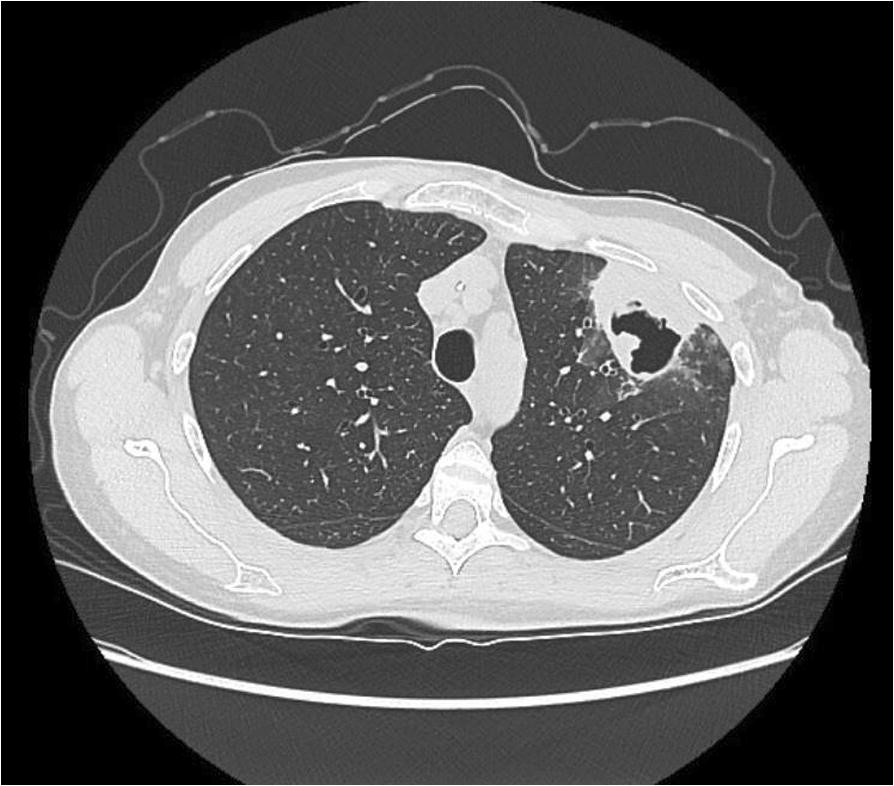
The tree-in-bud sign is a radiographic appearance seen on chest x-rays and CT scans that is indicative of pulmonary nodules or mass. The tree-in-bud pattern represents centrilobular branching structures that resemble a budding tree. 87 rows The tree-in-bud sign indicates bronchiolar luminal impaction with mucus pus or.
87 rows mid-bronchial lesion. The tree-in-bud sign is a nonspecific imaging finding that implies impaction within bronchioles the smallest airway passages in the lung. The tree-in-bud-pattern of images on thin-section lung CT is defined by centrilobular branching structures that resemble a budding tree.
Post-mortem radiograph of patient with active pulmonary tuberculosis demonstrating tree-in-bud lesion boxed area with smooth marginated bronchiole tree and. The tree-in-bud sign is a nonspecific imaging finding that implies impaction within bronchioles the smallest airway passages in the lung. Tree-in-bud refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree.
Typically the centrilobular nodules are 2-4 mm in diameter and peripheral within 5 mm of the pleural surface. The pattern reflects a spectrum of endo- and peribronchiolar disorders including mucoid.

Incidental Endobronchial Hamartoma In A Patient With Enchondroma Bmj Case Reports
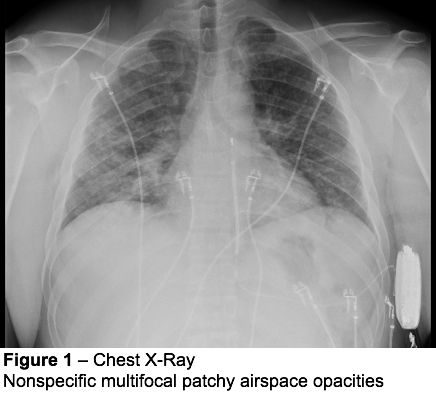
It Is Not Always Tuberculosis Tree In Bud Opacities Leading To A Diagnosis Of Sarcoid Shm Abstracts Society Of Hospital Medicine

Tree In Bud Pattern At Thin Section Ct Of The Lungs Radiologic Pathologic Overview Radiographics
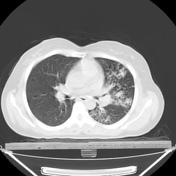
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Pattern At Thin Section Ct Of The Lungs Radiologic Pathologic Overview Radiographics
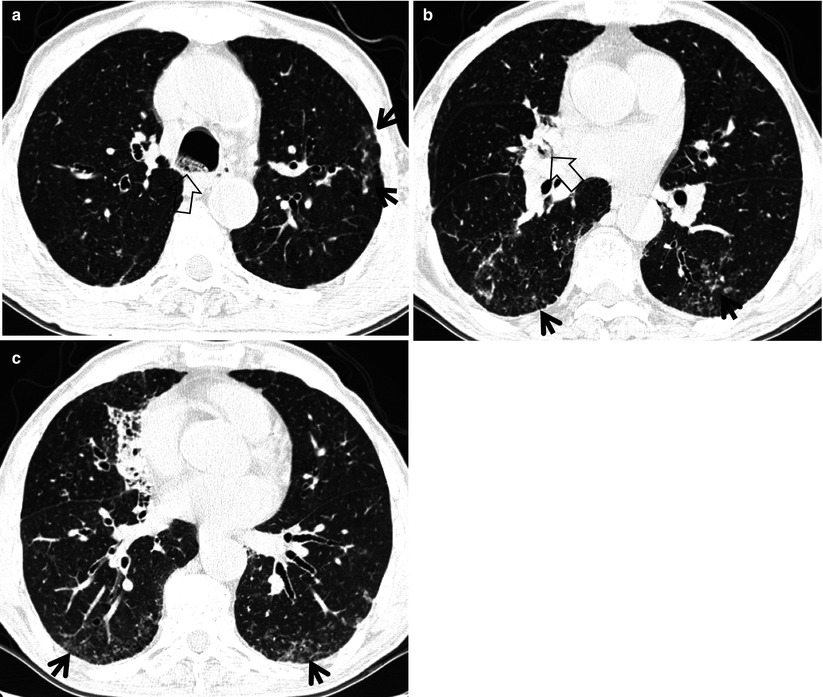
Tree In Bud Sign Radiology Key
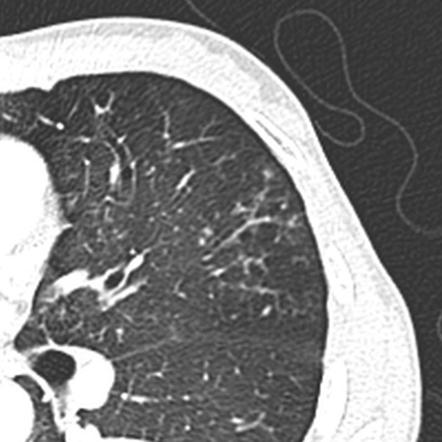
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Pattern At Thin Section Ct Of The Lungs Radiologic Pathologic Overview Radiographics
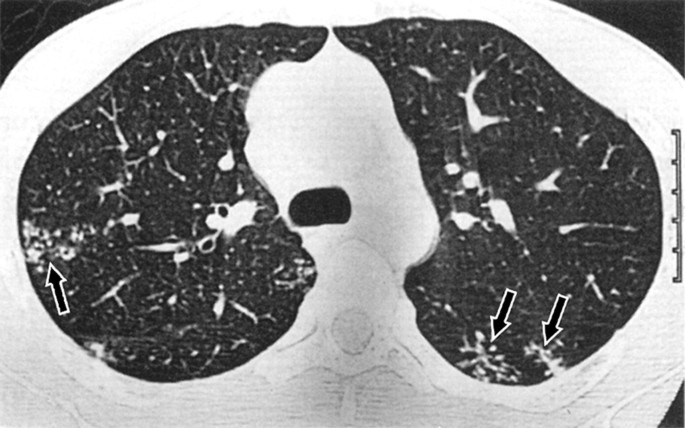
Patterns Of Lung Disease Springerlink

Tree In Bud Pattern Semantic Scholar

Intracavitory Lesion With Adjacent Tree In Bud Infiltrates Noted In The Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Sciencedirect
Assessment Of Disease Activity And Complications In Patients Of Pulmonary Tuberculosis By High Resolution Computed Tomography Sudan Journal Of Medical Sciences Sjms